A Dual BIOS motherboard is a computer motherboard with two separate BIOS chips. The first BIOS chip is the primary BIOS chip, and the second BIOS chip is the backup BIOS chip. If the primary BIOS chip fails, you can use the backup BIOS chip to boot the computer.
What is a dual BIOS motherboard?
Most modern motherboards come with two BIOS chips. One is a backup in case the primary BIOS becomes corrupted. The other is used to store custom BIOS settings or to revert the BIOS to default settings.
A dual BIOS motherboard offers extra protection from failed firmware updates, viruses, and hardware failures. If the primary BIOS becomes corrupted, you can boot from the backup BIOS and continue using your computer.
Some manufacturers offer a dual BIOS switch that allows you to select which BIOS chip is active manually. This can be useful if you want to experiment with different BIOS settings without affecting the stability of your system.
Dual BIOS motherboards are typically more expensive than single BIOS models. Still, they offer peace of mind for power users and enthusiasts who regularly update their BIOS or experiment with different settings.
How does a dual BIOS motherboard work?
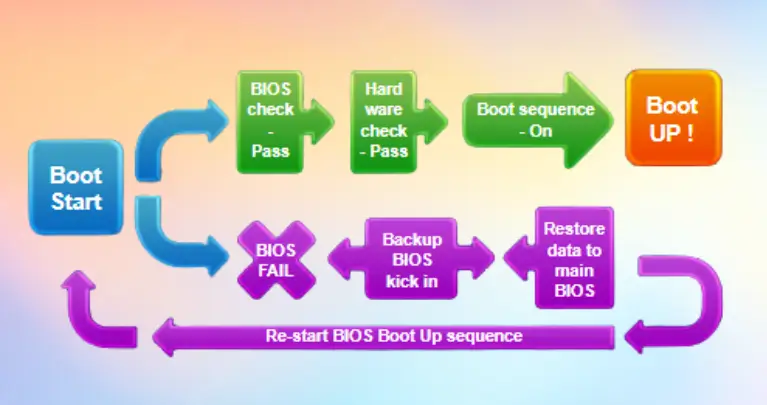
A dual BIOS motherboard is a computer motherboard that has two separate BIOS chips. This provides a backup in case one of the BIOS chips fails. You can also use it to store different firmware versions for different operating systems.
The benefits of a dual BIOS motherboard.
A dual BIOS motherboard is a PC with two sets of BIOS chips. The benefits of having a dual BIOS motherboard include increased protection against BIOS corruption and the ability to recover from a failed BIOS flash.
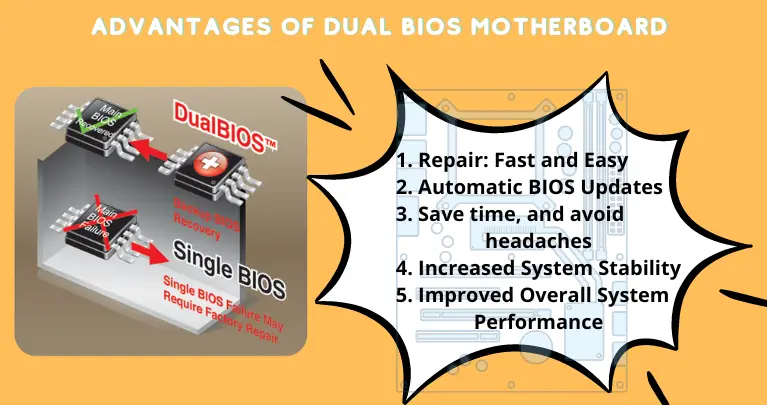
Benefits of Dual BIOS motherboard:
1. Repair: Fast and Easy: When a motherboard’s BIOS is corrupted, it cannot be easy to fix. A dual BIOS motherboard has a backup BIOS that it can use to repair the primary BIOS. This makes repairing a failed BIOS much easier and faster.
2. Automatic BIOS Updates: The dual BIOS motherboard benefit of automatically updating the BIOS without user intervention means that you will always have the latest version installed and ready to go. This can help prevent issues caused by outdated BIOS versions and ensure that your system runs at its best. Additionally, automated updates can help save time and hassle by taking care of the process for you.
3. Save time, and avoid headaches: When your motherboard has a dual BIOS, any corrupted data in the main BIOS can be backed up and replaced with the secondary BIOS. This helps to reduce service time and avoid any potential headaches that come with replacing your entire motherboard.
4. Increased System Stability: Motherboards with dual BIOS have an extra fail-safe that can help your computer recover from booting issues. If the primary BIOS becomes corrupted, the backup BIOS can take over and help your computer boot up successfully. This increases the stability of your system overall, making it less likely for you to experience any downtime.
5. Improved Overall System Performance: A dual BIOS motherboard offers improved overall system performance by providing a backup in case of corruption or failure. This can help prevent data loss and system downtime and give you peace of mind knowing that your system is always backed up.
Overall, having a dual BIOS motherboard provides an extra layer of protection for your PC and can be a lifesaver in case of a bad flash or power outage.
The disadvantages of a dual BIOS motherboard.
One disadvantage of a dual BIOS motherboard is that it can be difficult to recover if one BIOS becomes corrupted. Additionally, dual BIOS motherboards are more expensive than single BIOS boards.
How to choose a dual BIOS motherboard.
When shopping for a dual BIOS motherboard, you should keep a few things in mind.
- First, ensure that the motherboard you’re considering supports the type of CPU you have or plan to use.
- Second, check how many PCI slots are available on the motherboard. If you plan on adding many expansion cards to your system, you’ll need a motherboard with enough PCI slots.
- Finally, take a look at the BIOS features that are available on the motherboard. Some dual BIOS motherboards allow you to adjust the CPU voltage, clock speed, and other parameters.
How to install a dual BIOS motherboard.
A dual BIOS motherboard is a motherboard that has two separate BIOS chips. One of the BIOS chips is a backup BIOS; if the primary BIOS fails, the backup takes over. This is usually done by switching the motherboard to select which BIOS to use.
The advantage of having a dual BIOS is that if one of the BIOS chips fails, you can still boot up the computer and use it. The disadvantage is that if both BIOS chips fail, you will not be able to boot up the computer.
There are two ways to install a dual BIOS motherboard. The first way is to install it in “legacy mode”. In legacy mode, the two BIOS chips are independent; if one fails, you can still use the other.
The second way to install a dual BIOS motherboard is in “native mode”. In native mode, the two BIOS chips are linked together, and if one fails, the other automatically takes over. Native mode is more reliable than legacy mode, but computers do not as widely support it.
How to troubleshoot a dual BIOS motherboard.
You can use either BIOS to boot your system if you have a dual BIOS motherboard. However, if one of the BIOS chips becomes corrupted, you may not be able to boot your system. In this case, you can use the other BIOS chip to boot your system and then flash (update) the corrupt BIOS chip.
Conclusion.
If you’re looking for a new motherboard and want to be sure that you have the best possible protection for your system, you should consider getting a Dual BIOS motherboard. These boards come with two separate BIOS chips, which provide redundancy in case one of the chips fails. This means that you’re much less likely to experience any downtime due to a BIOS failure, and it also means that you can more easily recover from a bad BIOS flash.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do all motherboards have dual BIOS?
No, not all motherboards have dual BIOS. Some motherboards have a single BIOS chip, while others have two BIOS chips. Dual BIOS chips can provide a backup in case one of the BIOS chips fails.
Why does the motherboard have two BIOS chips?
The motherboard has two BIOS chips in order to provide a backup in case the primary BIOS chip fails. This is important because if the BIOS fails, the computer will not be able to boot up. In addition, having two BIOS chips provides an extra layer of protection against malicious attacks. If one chip is compromised, the other can still provide instructions to the computer on how to boot up safely.
Does ASUS have dual BIOS?
Yes, ASUS does have dual BIOS. This is a feature that allows you to have a backup BIOS in case the primary BIOS becomes corrupted.
How to know if motherboard has dual bios
If you’re not sure whether or not your motherboard has dual bios, there are a few things you can check. First, look for a physical switch on the motherboard itself. This switch will usually be located near the BIOS chip. If there’s no switch, you can also check the BIOS menu for an option to enable or disable dual bios. Finally, you can check the manufacturer’s website or documentation to see if your particular model of motherboard supports dual bios.
How to use dual bios on gigabyte
There are a few different ways to use dual BIOS on a Gigabyte motherboard. One way is to enable the dual BIOS feature in the BIOS settings. This will allow you to have two separate BIOS images on the motherboard, and you can switch between them using a switch on the motherboard. Another way is to use the Gigabyte DualBIOS utility, which will allow you to update both BIOS images at the same time.


![Why Motherboard Is Important? [Complete Details]](https://gamingwiser.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Why-Motherboard-Is-Important-450x235.webp)