VRM on a motherboard is made up of multiple parts. Among these components, VRMs are one of the most important ones.
A VRM is a large and expensive component that performs an uninterrupted power supply to the motherboard.
Connecting the VRM to the motherboard is a difficult task. Almost 20% of the motherboards are reported to have damaged VRMs.
In this article, we will give a short and straightforward introduction to VRMs, which can help you understand how VRMs work and how to connect the VRMs.
What is VRM on a Motherboard?
A voltage regulator module (VRM) is a small circuit board that regulates the voltage going to a computer’s CPU. It is usually located on the motherboard, near the CPU socket.
VRMs take DC voltages from the power supply and generate smaller DC voltages used by the CPU. VRMs can be found on laptops, desktops, servers, and workstations.
A voltage regulator module (VRM), sometimes called a power supply module (PPM), is a voltage regulator that delivers the microprocessor and processor the appropriate voltage, converting 3.3 V, 5 V, or 12 V to less voltage needed by devices, allowing devices with different voltage requirements to be mounted alongside each other.
There are two main types of VRMs: linear and switching.
Linear VRMs use a linear regulator to convert the input voltage into the desired output voltage.
Switching VRMs use a switch mode power supply (SMPS) to convert the input voltage into the desired output voltage. SMPSs are more efficient than linear regulators, but they generate more heat.
The number of phases in a VRM is also important. A single-phase VRM can provide enough power for most CPUs, but a multi-phase VRM is needed for high-end CPUs that require more power. Multi-phase VRMs distribute the power load among multiple phases, which helps to reduce heat generation and improve efficiency.
Choosing a VRM with too few phases or inadequate power can cause problems such as unstable voltages, reduced overclocking potential, and shorter component lifespan. If you are unsure which VRM to choose for your system, consult a qualified technician or motherboard manufacturer.
What does a VRM do?
A Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) is a small circuit board located next to the CPU socket on a motherboard. It regulates the voltage supplied to the CPU, providing the processor with the proper amount of power it needs to function correctly. Without a VRM, your CPU would not be able to function.
A VRM consists of MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors), capacitors, and other components that work together to regulate voltage. MOSFETs control the flow of electricity, while capacitors store and release electricity when needed.
The VRM is integral to your motherboard because it ensures that your CPU receives the correct amount of power. If the VRM isn’t working correctly, your CPU may not receive enough energy and overheat or underperform.
How does a VRM work?
A VRM is a Voltage Regulator Module, and it’s used to regulate the voltage going to the CPU (or APU in this case) of your motherboard. It’s made up of MOSFETs, Inductors, and Capacitors, and its purpose is to lower the voltage from your power supply so that it’s compatible with your CPU.
If you’ve ever overclocked a CPU, then you’ve probably increased the voltage to it using the BIOS settings; this is what the VRM does, but on a smaller scale and much more frequently.
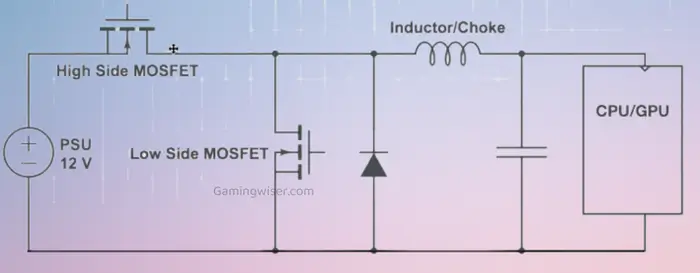
The MOSFETs act as switches that turn on and off rapidly (thousands of times per second) to regulate the voltage. They do this by allowing or stopping the current to flow through them; when switched on, the current can flow through them, and when switched off, it can’t. The longer they’re switched on, the higher the voltage will be.
The Inductors store energy in their magnetic field and are used to filter out any unwanted noise or spikes in the power supply. This helps to ensure that the voltage remains constant.
Finally, the Capacitors are used to store energy and provide a steady flow to the MOSFETs. This ensures that there’s no power drop when switching on and off.
What are the benefits of a VRM?
A VRM, or voltage regulator module, is a component of your motherboard that regulates the power delivered to your CPU. It does this by converting the alternating current (AC) from your power supply into the direct current (DC) needed by your CPU.
VRMs are essential to any motherboard, but they are critical on high-end motherboards and CPUs. This is because high-end CPUs require more power than lower-end CPUs, and a VRM that isn’t up to the task can cause all sorts of problems, from stability issues to crashes.
There are a few things that make an excellent VRM.
- First, it should have a high maximum current rating. This is the maximum amount of current that the VRM can supply to the CPU at any given time.
- Second, it should have a low maximum voltage drop. This is the difference between the voltage supplied by the VRM and the voltage that reaches the CPU. The lower the voltage drop, the less power is lost in transit between the VRM and the CPU.
- Third, a good VRM should have a low minimum load rating. This is the minimum amount of current flowing through the VRM to function correctly. If there isn’t enough current flowing through the VRM, it can overheat and break down.
- Fourth, a good VRM should have a high switching frequency. This is how often the VRMs transistors switch on and off and is measured in Hertz (Hz). The higher the switching frequency, the faster the transistors can react to changes in the voltage supplied by the power supply. A high switching frequency can lead to better stability and cooler operating temperatures.
- Fifth, good VRM will have low Rds(on) values and MOSFETs. Rds(on)is resistance caused by parasitic effects within MOSFETs when they are turned on. The lower Rds(on), the lower the resistance; thus, the lower the amount of wasted heat energy.
- Sixth, good VRMs will use drivers that can deliver high peak currents. Drivers are what control MOSFETs, and they need to be able to provide high peak currents to maintain proper regulation under heavy loads.
How to choose the right VRM for your motherboard?
When shopping for a motherboard, you’ll want to pay attention to the VRM. This stands for “voltage regulator module,” an essential part of the motherboard that regulates the voltage. A good VRM can save your motherboard from damage caused by overclocking, and it can also improve system stability.
There are a few things to look for when choosing a VRM for your motherboard:-
VRM Design: The physical design of the VRM is essential, as it determines how well the VRM can dissipate heat. A good VRM design will have a large heatsink that helps to keep the VRM cool, even when under heavy load.
Number of Phases: The number of phases determines how smooth the power delivery is to the CPU. A higher number of phases means there will be less voltage fluctuation, which is ideal for overclocking.
Power Delivery Components: The quality of the power delivery components is also essential. These components include the MOSFETs, chokes, and capacitors. Higher quality components will improve power delivery and more stability when overclocking.
How important are VRMs on a motherboard?
VRMs on a motherboard are important because they provide power to the CPU. Without VRMs, the CPU would not be able to function properly. VRMs are also responsible for regulating the voltage that is sent to the CPU.
If the voltage is too high, it can damage the CPU. Too low, and the CPU will not be able to perform at its best. That’s why having high-quality VRMs is important for ensuring that your CPU runs smoothly and efficiently.
Conclusion
VRMs on a motherboard are responsible for providing CPU power. They are typically located near the socket and comprise several components, including MOSFETs, inductors, and capacitors. VRMs are essential when choosing a motherboard for your PC, as they can significantly affect performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do VRMs work?
VRMs convert the voltage from the power supply into the voltages required by the CPU and other components. They are typically made up of MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors), inductors, and capacitors.
What causes VRM problems?
There are a few different things that can go wrong with VRMs. The most common problem is excessive heat, which can cause MOSFETs to fail. Other issues include inadequate cooling, poor quality components, electrical shorts, and manufacturing defects.
How do I know if my VRMs are failing?
The most common symptom of VRM failure is instability – your computer may randomly reboot or shut down, or you may see artifacts (strange lines or shapes) on your screen. You may also see smoke or sparks coming from your motherboard. If you suspect your VRMs are failing, you should immediately shut down your computer and contact a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair.
Can I replace my VRMs myself?
Replacing VRMs is generally not recommended for people without experience working with electronics. Finding replacement parts that are compatible with your motherboard can be challenging, and soldering wires in place is delicate work that requires a steady hand and attention to detail. If you’re not confident in your ability to do the job correctly, it’s best to leave it to a professional.


![Why Motherboard Is Important? [Complete Details]](https://gamingwiser.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Why-Motherboard-Is-Important-450x235.webp)